Reflectors
 24 марта, 2014
24 марта, 2014  admin
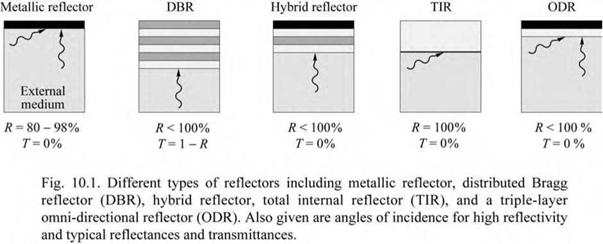
admin Ideal reflectors incorporated into a device structure should have (i) high reflectivity, (ii) a sufficiently broad spectral range of the high-reflectivity band, (iii) omnidirectional characteristics, and (iv) low resistivity (provided current flows through the reflector). It is a question of great practical and intellectual interest what type of reflector best meets these multiple requirements.
Different types of reflectors are shown in Fig. 10.1 including a metallic reflector, distributed Bragg reflector (DBR), hybrid metal-DBR, reflectors based on total internal reflection (TIR), and an omni-directional reflector. The characteristics of the different types of reflectors will be discussed below.
|
|
An external medium is indicated in the figure. In an LED structure with a reflector, the external medium is a semiconductor. The external medium has a significant influence on the reflector properties. For example, the reflectivity of a metal-semiconductor reflector is lower compared to a metal-air reflector.

 Опубликовано в
Опубликовано в