Mechanical Behavior of Welds
 8 февраля, 2014
8 февраля, 2014  admin
admin From the industry point of view, the most critical mechanical effects of welding are cracking, distortion and buckling. The influence of welds on crack propagation in stress corrosion cracking, fatigue and fracture is also a concern.
The difficulties of obtaining relevant material properties, in making experimental measurements to validate predictions and the complexity of the mathematical descriptions have all inhibited progress.
In practice however there are many aspects of welding that have made the rigorous analysis of welds a challenging procedure. At the macroscopic level a weld can be considered to be a thermomechanical problem of computing transient temperature, displacement, stress and strain. At the microscopic level, it can be considered to be a metal physics problem of computing the phase transformations including grain growth, dissolution and precipitation.
In addition to the capability of computing the microstructure and fracture mechanics, this will require a model for hydrogen diffusion along dislocations and grain boundaries as well as volume diffusion. Hydrogen diffusion can be a function of stress. It will require a model of hydrogen trapping, including a model for inclusions [15].
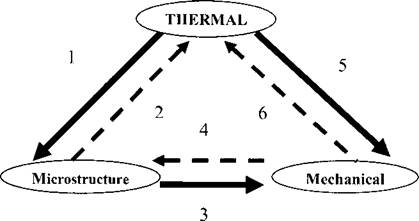
The mechanical behavior of welds is sensitive to the close coupling between heat transfer, microstructure evolution and thermal stress analysis. Figure 1-5 describes the coupling between the different fields in the modeling of welding. Although the effects of microstructure and stress-strain evolution on heat transfer are not large, the effect of temperature on the microstructure and thermal stress is dominant. In addition, the coupling between microstructure and thermal stress can be strong and subtle (the dominant couplings in welding are shown with bold lines, the secondary couplings are shown with dotted lines, Figure 1-5). Phase transformations, can dominate the stress analysis, [6 and 15].
The modeling of the fluid flow is not included in Figure 1-5, because the effect of the fluid flow on the deformation and stress field can be considered as negligible [24]. However, if geometrical changes close to the weld pool are of primary interest, modeling the fluid flow will be essential.
|
|
Coupling Explanation
1 Transformation Rates (microstructure evolution depends on temperature).
2 Latent heats (each phase transformation can have an associated latent heat). They act as a heat sink on heating and as a heat source on cooling.
3 Phase Transformations (volume changes due to phase changes, plastic and elastic material behavior depend on the microstructure of material).
4 Transformation Rates (microstructure evolution can particularly martensitic and bainitic transformations, depend on mechanical deformation).
5 Thermal Expansion (mechanical deformations depend on temperature).
6 Plastic Work (mechanical deformation generates heat in the material and changes the thermal boundary conditions). In most welding processes this effect is very small.
Figure 1-5: Coupling between different fields in welding analysis.
In the past ten years considerable progress has been made in developing numerical methods to solve this coupled problem with increasing speed and accuracy.
Realistic welds may involve numerous passes, each of which contributes to the mechanical and metallurgical effects. Interactions be
tween thermal, mechanical, metallurgical, and in the molten pool chemical and fluid processes are complex.

 Опубликовано в
Опубликовано в